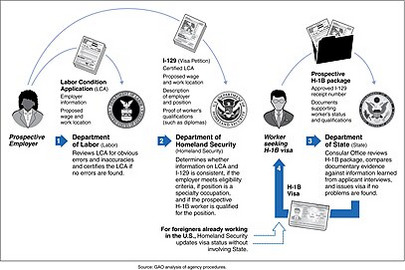
H-1B visa
The H-1B is a classification of non-immigrant visa in the United States that allows U.S. employers to hire foreign workers in specialty occupations, as well as fashion models, or... Wikipedia
- Type: Non-immigrant work visa
- Purpose: Employment of foreign workers in specialty occupations
- Enacted: Immigration Act of 1990, roots in H-1 visa from Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952, modified by American Competitiveness in the Twenty-First Century Act of 2000 (AC21) and subsequent legislation
- Eligibility: Bachelor's degree or higher in specific specialty, Job offer for a specialty occupation, Employer sponsorship
- Duration: Initially up to 3 years, extendable to 6 years, further extensions possible under certain conditions (e.g, pending green card applications)
- Annual cap (limit): New visas/statuses, 65,000 regular cap, 20,000 additional for U.S. advanced degree holders, 1,401 for Chilean nationals (H-1B1), 5,400 for Singapore nationals (H-1B1), Certain employers are cap-exempt, e.g, higher education institutions, nonprofit research organizations, Extensions/renewals are not capped
- Dependents: Spouse and unmarried children under 21 eligible for H-4 visas
- Work Authorization: H-1B holder: Allowed to work for sponsoring employer, H-4 dependents: Eligible if H-1B spouse has approved I-140 immigrant petition or H-1B status beyond 6 years under AC21
- Dual Intent: Allowed (can pursue permanent residency)
- Oversight: U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS)
- Data source: DuckDuckGo